Using a Secure Environment to Enable Community-level Suicidality
Research for the CLPsych 2021 Shared Task - 9/20 to 5/21
Progress on NLP for mental health — indeed, for healthcare in general — is hampered by obstacles to shared, community-level access to relevant data. We report on what is, to our knowledge, the first attempt to address this problem in mental health by conducting a shared task using sensitive data in a secure data enclave. Participating teams received access to Twitter posts donated for research, including data from users with and without suicide attempts, and did all work with the dataset entirely within a secure computational environment. We discuss the task, team results, and lessons learned to set the stage for future tasks on sensitive or confidential data.
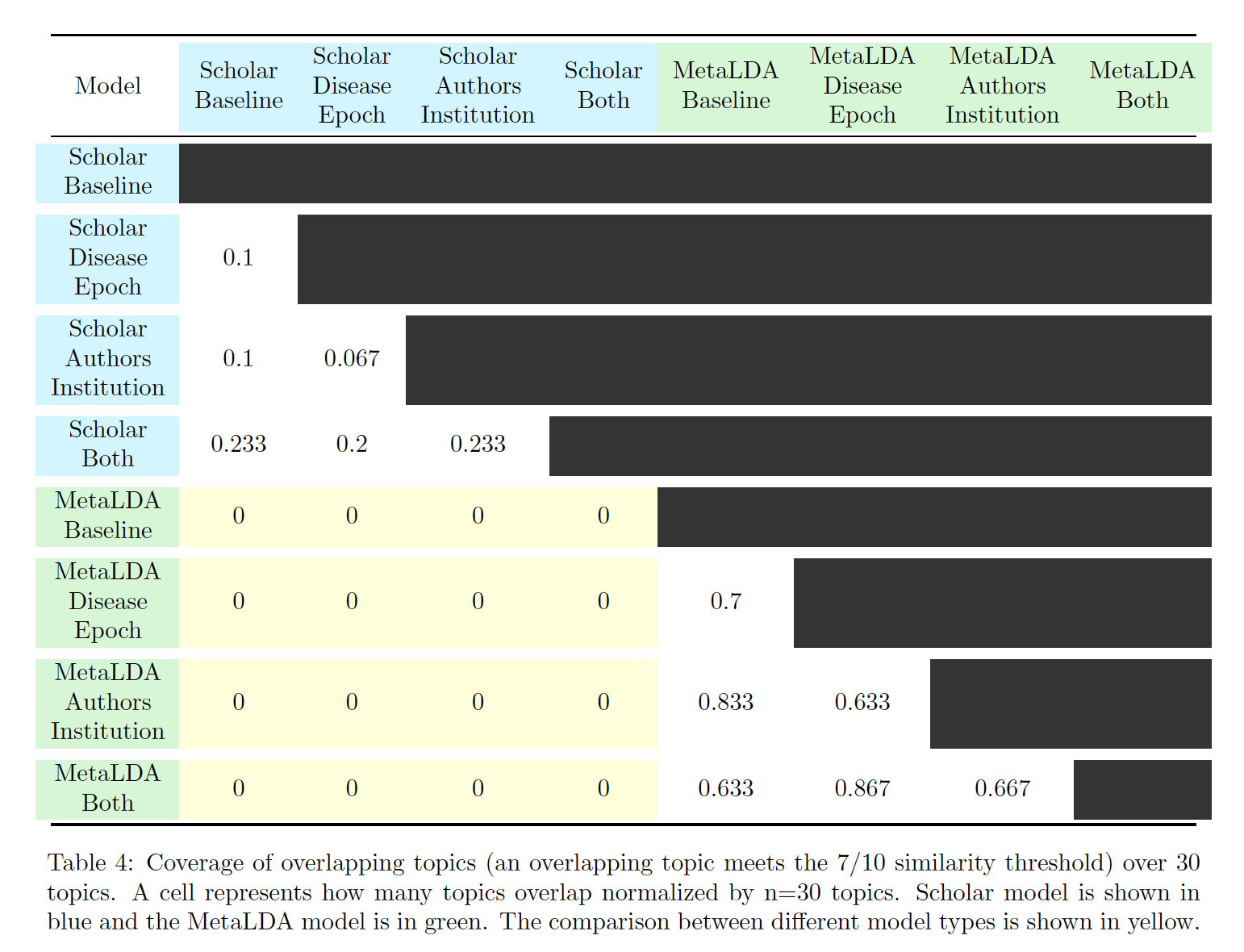
Evaluating Metadata-Driven Approaches to Topic Modelling - 3/20 to 5/20
The COVID-19 pandemic has caused an increase in scholarly articles published about the coronavirus. It has been difficult for the medical community to keep up with the rate that articles are being published. This has created a demand for data mining tools and text analysis techniques to sort through the published findings. Identifying the various topics within the dataset can help researchers group documents together and more quickly identify relevant articles.
Several recent papers in the past few years have proposed different ways of incorporating known metadata attributes into topic models that previously only accounted for the word tokens in the documents themselves. In this project, we explored two such topic models which incorporate known metadata attributes, SCHOLAR and MetaLDA. Incorporating metadata in a topic model is a natural way to include additional information since humans also use metadata when processing text. We chose two metadata attributes about the documents: time period of publication and author's institution. Using these, we explored the effects of both metadata attributes across both models and compared this with the topics generated from similar models without additional metadata. Our overall goal was to identify topics relevant to risk factors associated with coronavirus diseases (one of the 'tasks' from the original Kaggle challenge) and to identify a model which was better at this task. We manually surveyed the output topics to assess if we had been successful.
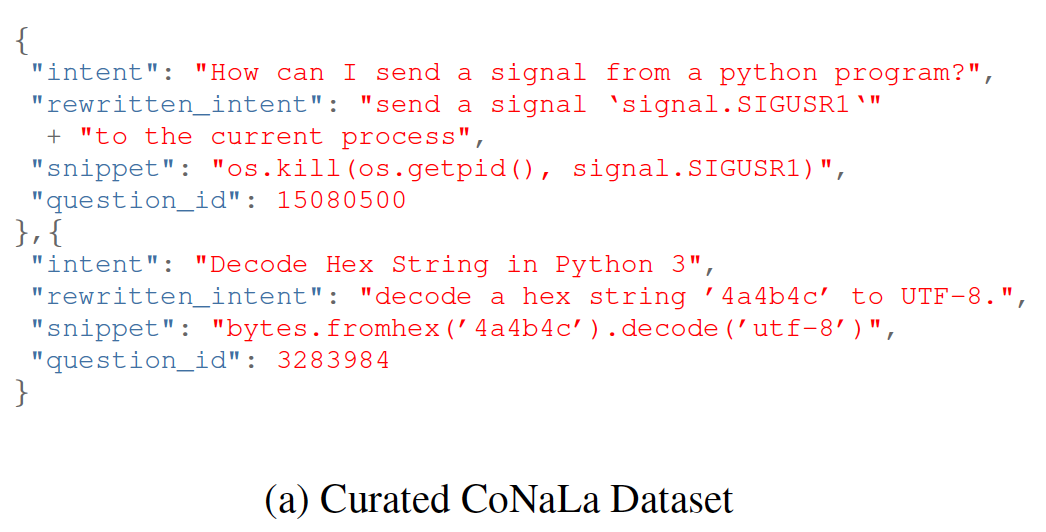
Analysing a Natural Language to Code Translation System
Applied to Spanish Queries - 9/19 to 12/19
Generating code from natural language is an important task, as often times, people are able to verbally state their intention but are unable to translate this intent into code. With the advent of machine learning, models are able to convert natural language into code. However, these approaches only address this challenge in English and not in other languages. In this paper we explore how current methods of code generation from natural language perform when generating code from natural languages other than English, specifically Spanish. While our experiments show lower BLEU score on Spanish datasets than English datasets, we do not believe we can conclude that the evaluated model generally performs worse on Spanish than English due to concerns about the quality and quantity of our Spanish data.
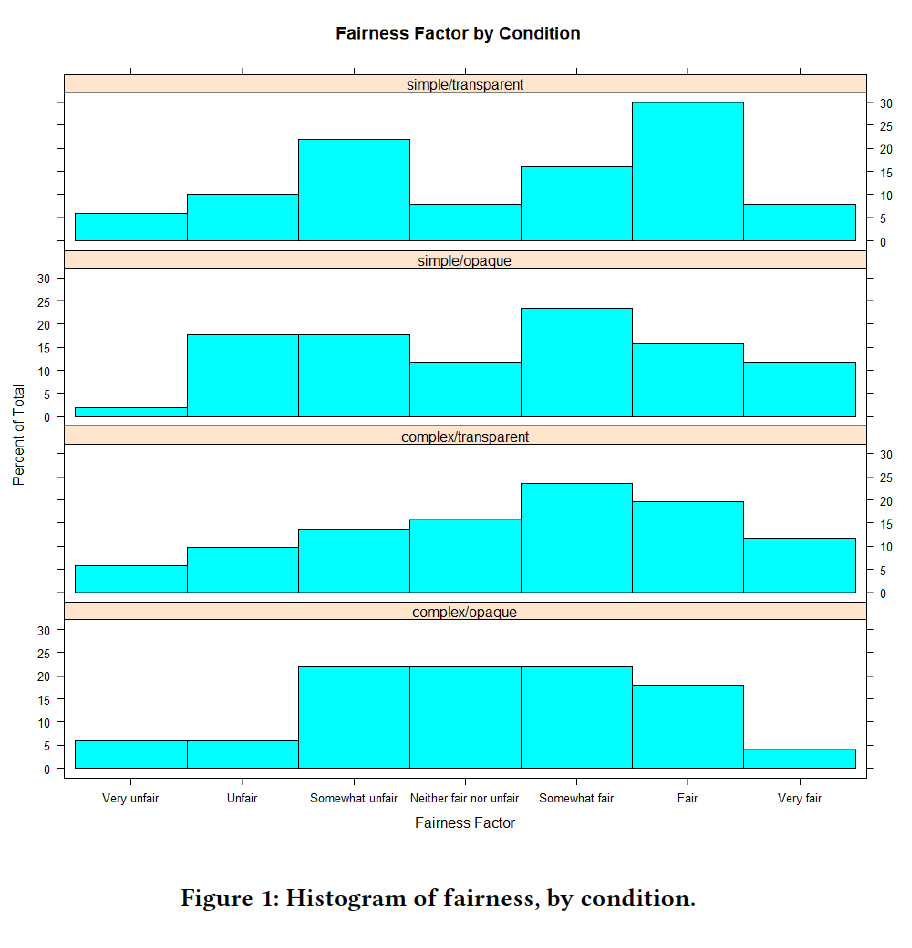
Perceptions of AI in Hiring - 9/18 to 12/18
The primary goal of this study is to answer the question of what it means for a ranking algorithm to be fair in the context of hiring. This question has become more significant in recent years, as many employers now use Applicant Tracking Systems (ATS) to recruit, screen, and rank job applicants. ATS often include a wide range of tools for tasks including parsing resumes, administering custom application forms, managing applicant data, screening and sorting applicants, and communicating with applicants
Participants were asked questions on their perceptions of the fairness and trustworthiness for a variety of situations. We also asked questions about participants emotional response. After performing our study and follow-up analysis, we were unable to confirm any of the hypotheses we identified in our initial work.
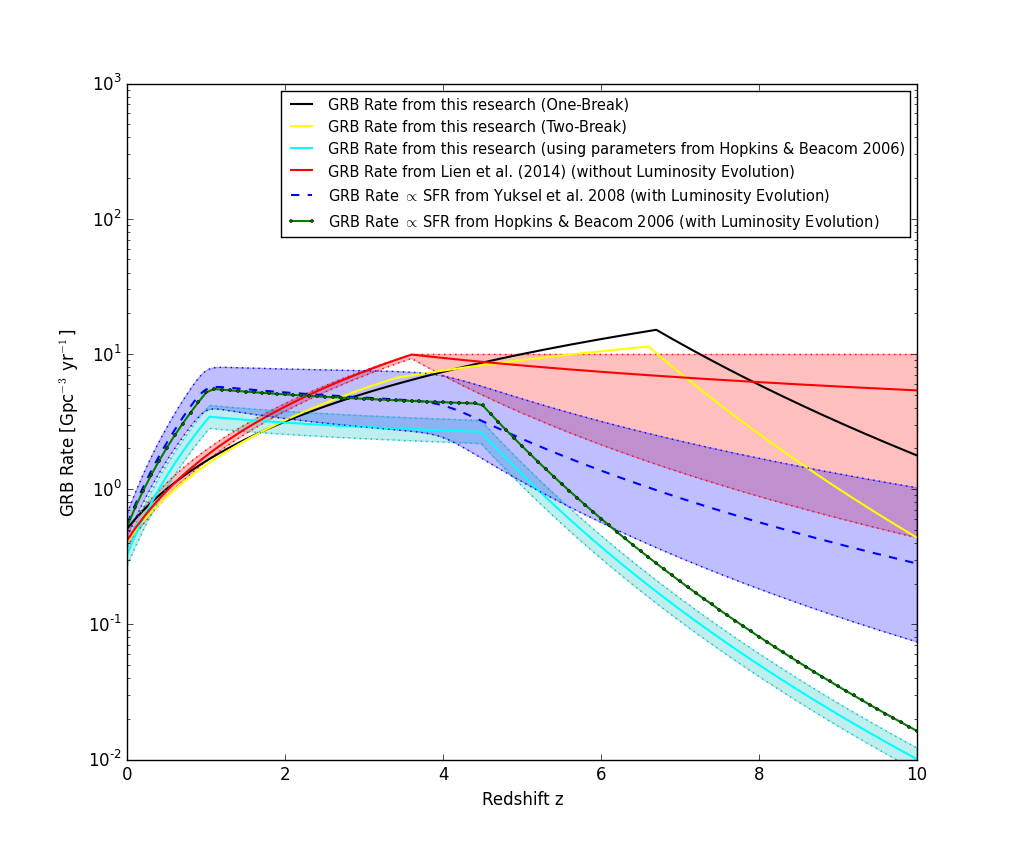
Bayesian Analysis of Swift GRB - 5/16 to 9/17
Different efforts in measuring star formation rate (SFR) have produced results differing by more than an order of magnitude. The rate of gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) could be a more direct way to measure SFR in comparison to other methods. GRBs are the most energetic astrophysical object in the Universe; they can be seen at high redshifts above ~6. This unique characteristic makes them a rare tool that could provide insight to the challenge of measuring the SFR of the early universe.
To better measure the SFR using long GRBs, it is important to account for the detection efficiency of Swift as a function of redshift. Swift uses a complex trigger algorithm with more than 500 trigger criteria, thus introducing complicated selection effects on GRBs. Recently in Graff et al (2015), the Swift BAT triggering algorithm was modeled using machine learning algorithms and the detection efficiency of Swift was measured.
In this research, we conducted a Bayesian study of the GRB rate distribution. We considered two models for the GRB rate: the original model from Graff et al (2015) containing only one break in the redshift function and the new model using a second break point in the redshift. The two break function allows a more direct comparison with most estimates of the SFR which also uses a double-broken-power-law model.
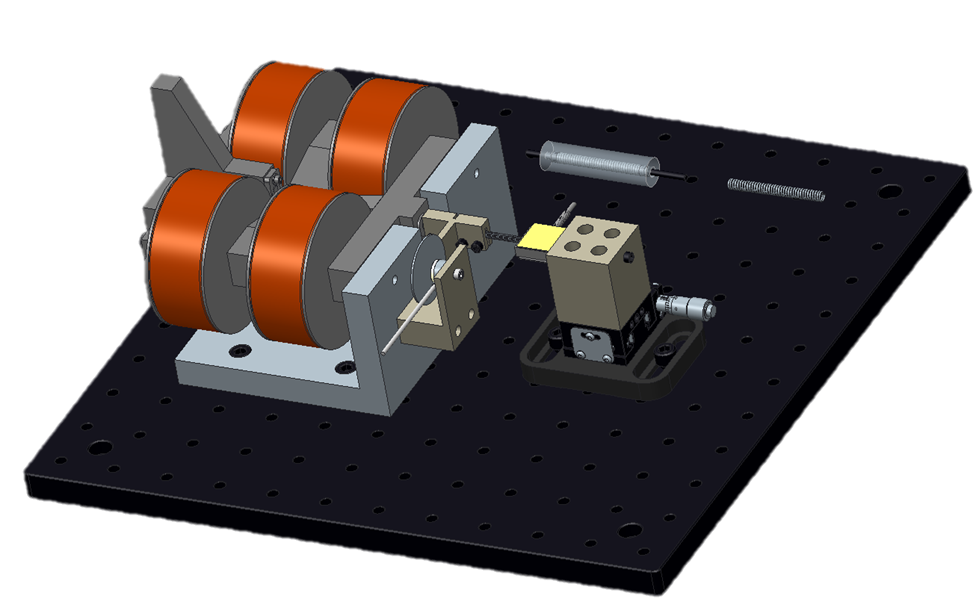
Magnetic Shape Memory Alloy Actuator for Nano-Positioning - 6/15 to 8/15
The goal of this project is to design, manufacture, and test a precision actuator based on new Magnetic Shape Memory Alloy (MSMA) material for space applications. MSMAs have been gaining attention since they perform better than current crystal materials used for precision actuators. MSMA have larger strains, higher stiffness, higher bandwidth, and lower amplifier volt-amp requirements compared to other materials. They require no lubrication and can run at cryogenic temperatures, thus allowing them to function for millions of cycles.
In the martensitic phase, MSMA is composed of different areas with alternating orientations of the easy axis of magnetization, called the twin variants. When a magnetic field is applied to the material, there is growth in the variants aligned with the field. This causes an overall lengthening of the sample. When the field is removed, the elongation is self-supported until an external force is applied to restore the original shape.
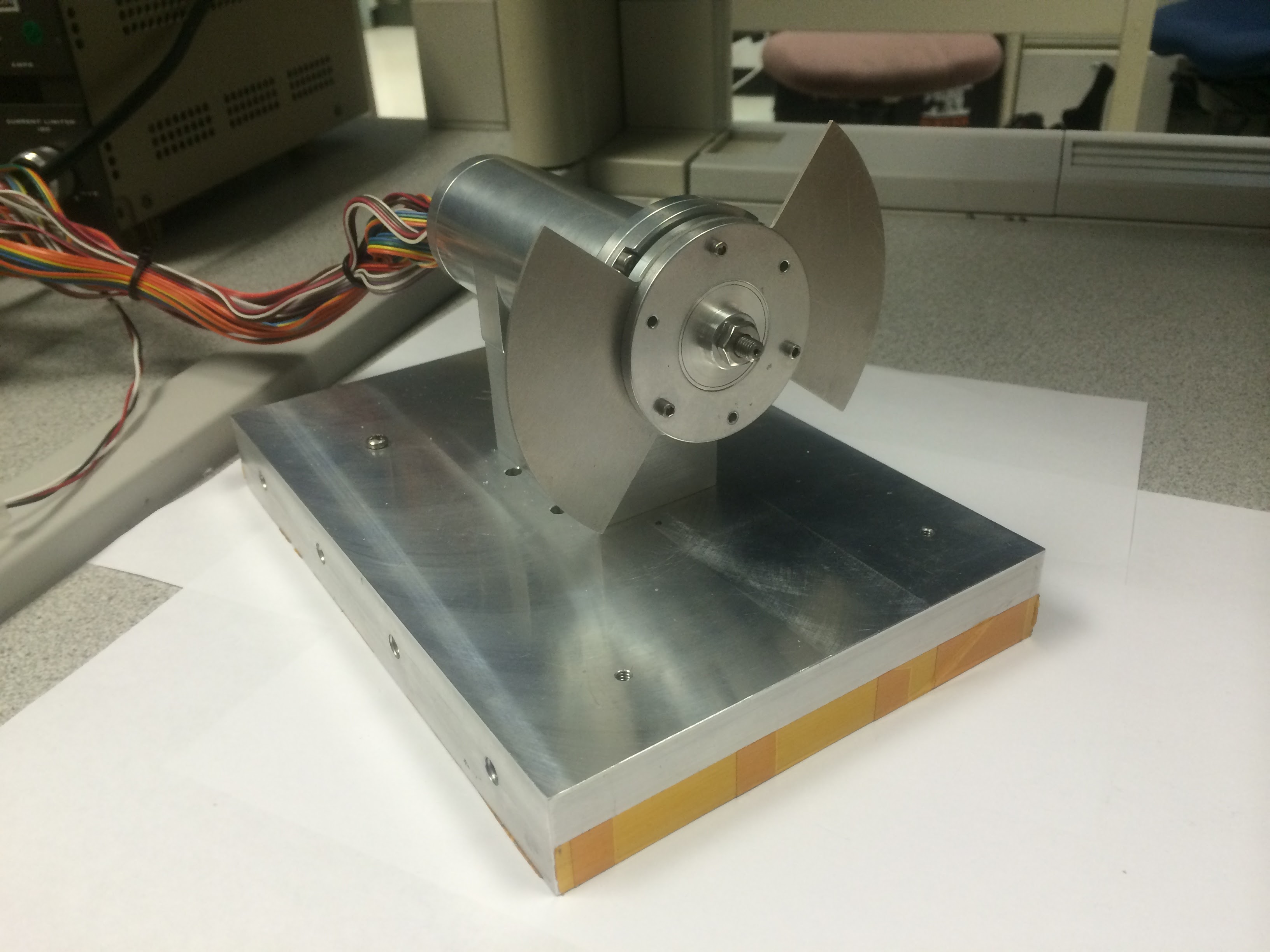
Magnetic Bearings for Space Flight Applications - 6/14 to 8/14
The goal of this project is to reconstruct and operate an existing magnetic bearing system that was developed by the Electromechanical Systems Branch. During the mid 90’s, HIRDLS EOS-CHEM (Earth Observing System-Chemistry) required an optical chopper that needed to be operated at 5,000 rpm throughout the mission life. Due to concerns that mechanical bearings might not be able to meet the life requirement, a magnetic bearing based optical chopper was developed as a parallel effort, but was never flown. Magnetic bearing can reduce vibrations, allow higher precision, eliminate friction and lubrication, and have a longer life compared mechanical bearing.
Reconstruction of the magnetic bearing system required understanding all the details of the magnetic bearing mechanism, electronics, and controller hardware and software. This required discussions with the engineers who were originally on the project, digging into documentation that was available, and consulting with dSPACE technical support. Since there is a multiplicity of sensors, windings, driver circuits, sensor processing circuits, etc., these all needed to be identified with the magnetic bearing coordinate system. A harness was designed to connect between the electronics and a dSPACE controller. Matlab/Simulink is where the controller algorithm resides. Sensor signal voltage range and scale factor was determined, as well as magnetic bearing parameters, and all circuit gains, in order to develop the closed loop control system. This effort will lead future magnetic bearing space flight application.
